Antibody

1. Definition and technological trends of antibodies
Antibodies, proteins produced by B cells, are essential for defending the body against foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses. The delicate balance between antigens and antibodies is crucial for maintaining health. When this balance is disrupted, diseases can occur. While the immune system can often restore equilibrium, chronic conditions like cancer and autoimmune diseases can overwhelm it.
To address these challenges, scientists have developed therapeutic antibodies using genetic engineering. These engineered antibodies have revolutionized the treatment of various diseases, particularly cancer and autoimmune disorders. The market for antibody therapeutics has experienced significant growth, with eight of the top ten best-selling drugs in 2018 being antibody-based. This market is expected to continue expanding rapidly, reaching USD 300 billion by 2025.
2. Current antibody research topics in our lab
2-1) Research on developing innovative antibody drugs
To address unmet medical needs, we aim to identify therapeutic antibodies with therapeutic potential by conducting in-depth analyses of the pathological mechanisms of target proteins. To establish optimal development strategies, we are systematically analyzing the mechanisms of action (MOA) and clinical trial data of various drugs, and designing target-oriented, customized research.
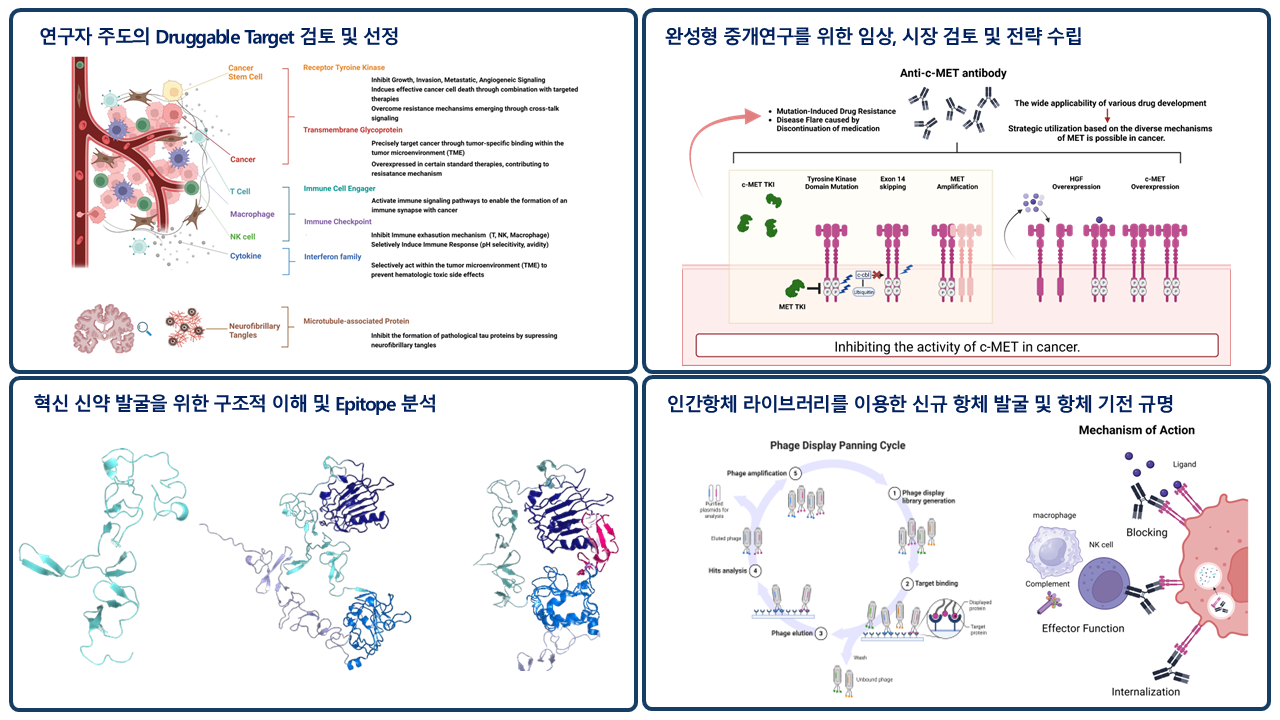

2-2) Development and research of immune checkpoint inhibitors
Our research is focused on developing a novel immune checkpoint inhibitor that can target specific immune cell subtypes to enhance immune response. The developed antibody has been patented and its sequence analyzed to secure intellectual property rights. We are utilizing an existing bispecific antibody platform and a CHO cell expression system for antibody production and conducting efficacy evaluations. The figure on the left illustrates the various immune checkpoint inhibitor targets involved in the tumor microenvironment, and our drug development strategies target specific immune cell subtypes for each target.
2-3) Development of antibody-cytokine therapeutics
Our research focuses on developing immunocytokines to transform cold tumors into hot tumors. By conjugating type 1 interferons with targeted antibodies, we aim to create immunocytokines that can directly kill cancer cells and indirectly activate immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, leading to enhanced anti-tumor efficacy.


2-4) Development of novel anti-cancer treatments based on Omomyc and asymmetric siRNA
– Omomyc fused with antibody
Our objective is to design a therapeutic intervention that targets and inhibits the overexpressed MYC protein in cancer cells. By modulating transcription, we aim to suppress cell growth, proliferation, and ultimately induce apoptosis.
– Asymmetric siRNA conjugated with antibody
Our objective is to develop a therapeutic strategy targeting genes that promote cancer cell induction and growth, and to induce apoptosis by degrading the corresponding mRNA.
